In 1991 or 1992, I took part in a Neuro Linguistic Programming practitioner training led by Ian McDermott, the founder of International Teaching Seminars. Among the many concepts and strategies he taught was the TOTE (Test–Operate–Test–Exit) model depicted below.

Read about George A. Miller and TOTE
The same principle is found in the field of cybernetics, the origin of which predates that of TOTE:
I participated in the NLP practitioner training while making the transition from the world of advertising and marketing to the worlds of innovation and organisational change. At the time, innovation and change were barely related and each had its own theories, its own language, and its own practices and practitioners. The field of change management was in its infancy — Daryl Conner’s groundbreaking book Managing at the speed of change first saw the light of day in 1993 — and organisational change work was in the hands of organisation development (OD) people.The field is named after an example of circular causal feedback—that of steering a ship (the ancient Greek κυβερνήτης {kybernḗtēs} means “helmsperson”). In steering a ship, the helmsperson adjusts their steering in continual response to the effect it is observed as having, forming a feedback loop through which a steady course can be maintained in a changing environment, responding to disturbances from cross winds and tide.
Source: Wikipedia — Cybernetics
In the early 1990s, there was much talk in the OD world about change being a journey from current reality to a desired future — a cumbersome and not wholly accurate description, given that change is not a journey (this is just a metaphor) and that what really needs to be created is a desired present state. Whether at work or in their personal lives, people want what they want now, not in some hypothetical future that never arrives.
Around the same time, I stumbled upon a copy of an in-house publication produced by Gemini Consulting, a high profile and influential change management firm that evolved into CapGemini. The authors of the publication didn’t talk about current reality and desired future. Instead, they used the punchier As-Is and To-Be. Today, these terms are widely used and unremarkable, but this was not the case in 1992.
What happened next was more like a thought experiment than a deliberate attempt at creating a new term. I wondered if As-Is and To-Be could each be reduced to three letters. My first attempt yielded Got and Want: accurate labels, but a little too colloquial for the business world and still four letters in the second word. Then inspiration struck. Got became Now, Want became New, and Now-to-New came into being.
The seven kinds of Now-to-New work
Read the article The seven kinds of Now-to-New work
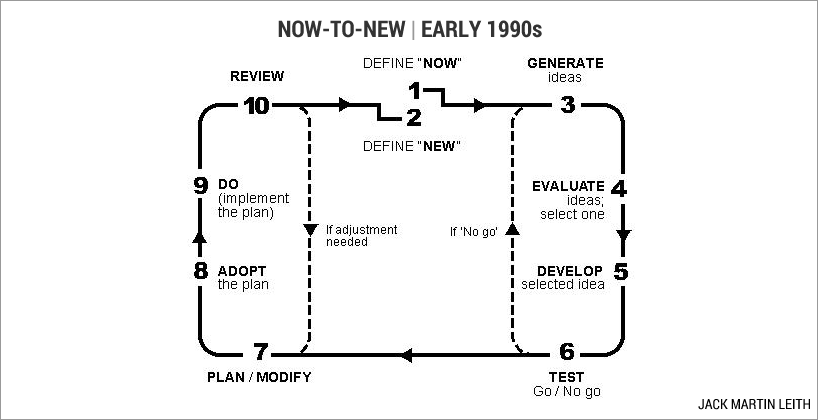
Evolution of the Now-to-New project model
Version 1 | Early 1990s
There is more to this model than meets the eye. For example, adoptability and implementation factors are considered when evaluating ideas.
Version 2 | Early 2000s
Non-linear.
Focus is on system-wide value generation.
Considerable but unintended overlap with generic design thinking approach:
- Specify Requirements corresponds with the design thinking phases Empathise and Define
- Design Concepts <> Ideation
- Conduct Experiments <> Prototype and Test
- Make Plans <> Implement
- Take Action <> Implement

Version 3 | 2010s
Here we have the Creative Lifecycle model, which is analogous to human procreation, development and maturity.
Readiness makes its first appearance.

Version 4 | 2023
Overall approach is given the name Newcreate.
Central thesis: Humans are mind-body-spirit instruments for creating that which generates value for others.
The purpose of the image below is to enable entrepreneurs and professional innovators to associate the creative powers of Imagination, Conceptualisation, Materialisation and Realisation with the main areas of work covered by a typical innovation programme.

Full exposition: How to put Newcreate into practice
Read about the seven creative powers
Continue reading
Now-to-New
Newcreate and other Now-to-New methods
The seven kinds of Now-to-New work
The three Now-to-New action modes: creating alone, creating together and helping others create
Related topics
How does Newcreate compare with design thinking?
How Newcreators use mind, body and spirit to create the new and enrich the worldn
Index to entire site (60+ pages)
Search the site
Not case sensitive. Do not to hit return.